Here's everything you need to know to use and manage Search on Windows 11.
When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Here’s how it works.

On Windows 11, Search is the feature that allows you to find virtually anything on your computer, including files, apps, settings, and answers to questions through web results. Also, because of its deep integration with Microsoft services, Search can show you results from OneDrive, Outlook, SharePoint, and others.
Although the Search experience has received many improvements on Windows 11, it can be only efficient if it's configured correctly and you know every shortcut to find what you are looking for quickly.
This guide will walk you through everything you need to know to use, manage, and fix problems with Search on Windows 11.
On Windows 11, there are multiple ways to access Search. You can open the Start menu and use the Search box at the top of the page.
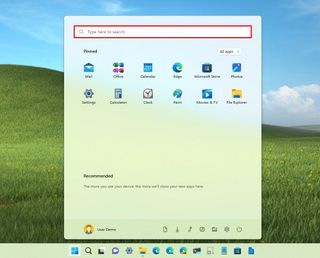
Or you can open the Search home by clicking the magnifier icon in the Taskbar or using the "Windows key + S" keyboard shortcut.
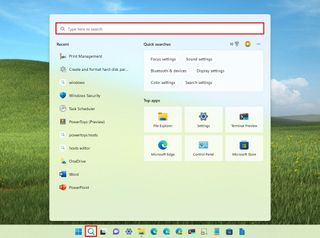
If you launch a query from the Start menu, the system will switch to Search home experience as you click the box.
For even quicker access to Search, you can press the Windows button on the keyboard and start typing to perform a search.
All the latest news, reviews, and guides for Windows and Xbox diehards.
By submitting your information you agree to the Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy and are aged 16 or over.
Although you can type anything, and the system will return the top results for apps, settings, files, or web results, you can use a few filters to help you narrow down the search. For example, when performing a query, you can click one of the filters, such as apps, documents, web, folders, music, photos, settings, etc.
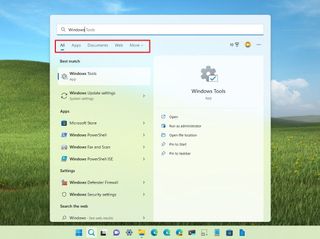
Alternatively, you can also type the query with the filter to narrow down the search. For example, if you want to search for a specific document, you can type something like "Documents: Windows," and the query will show only the files that match the keyword you specified.
You can also use these options, "app:" "web:" "email:" "folders:" "music:" "people:" "photos:" "settings:" and "videos:"
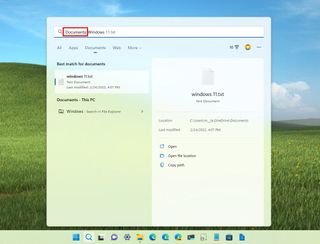
To find files and folders on File Explorer, you can click the search box in the top-right corner. Or you can use the "Ctrl + F" keyboard shortcut to focus on the search box, type the query, and press Enter.
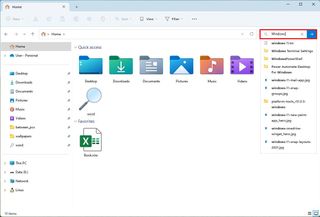
As you start typing in the box, you will notice a list of your recent searches, which you can select to get to recent searches quickly. (You can always click the remove button next to the item to delete it from the list.)
Once on the result page, the command bar will bring up the "Search options" menu, which allows you to change the scope to only search the current folder or subfolders.
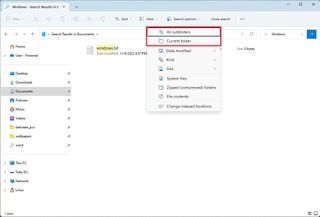
You can also filter the search by date modified, kind (document, picture, folder, video, music, etc.), and size.
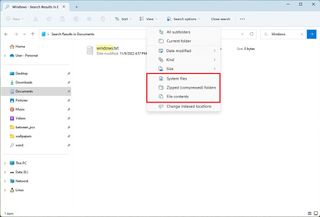
If you want to speed up the search for personal files, you can open the "Search options" menu and clear out the "System files" option.
The "Search options" menu also includes the "Zipped" option to allow the system to look inside compressed folders and the "File contents" option to look inside the file to return a result.
In addition, it's possible to use the "Sort" menu to sort the results by name, date modified, type, and more.
For example, if you're searching for a specific picture, you can use the "View" menu and the "Extra large icons" option to make the file easier to find.
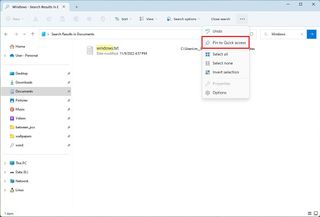
If you know you will perform the same search frequently, you can also open the See more (three-dotted) menu and select the "Pin to Quick access" to save the search and make it available from the left pane.
In the Taskbar, you will find the Search button, which gives you quick access to Search home, and if you hover over the button, it will also display quick access to your recent searches. However, since you can also perform searches from the Start menu, you can always disable the button.
To enable or disable the Search button in the Taskbar, use these steps:
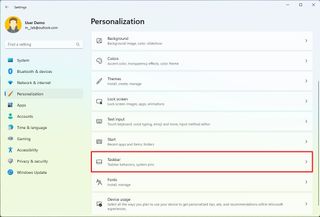
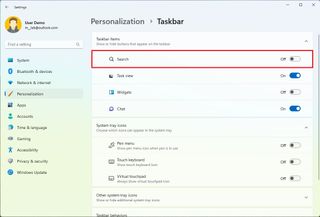
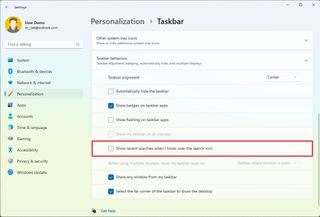
After you complete the steps, the button will no longer be available in the Taskbar. However, you can continue to access the experience from the Start menu or using the "Windows key + S" keyboard shortcut.
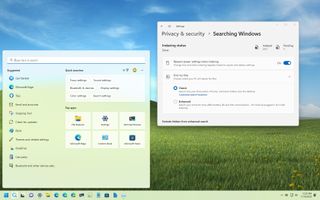
The "Search permissions" settings allow you to control how Windows 11 should search and present the results.
Control safe search settings
In addition to results for apps, files, and settings, Windows 11 also offers web results for queries you type. However, the web can show unfiltered results that may include unsuitable content, but you can always change the restriction level.
To change the search safety level, use these steps:
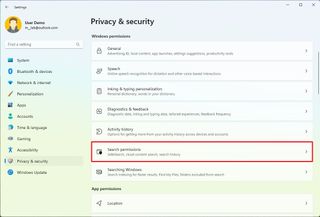
Once you complete the steps, the search results for the web will be limited to the safety level you selected.
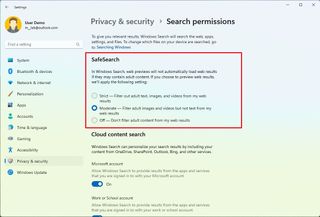
Control cloud search settings
When using the Search experience, the system can also show results from content in OneDrive, SharePoint, Outlook, Bing, and other Microsoft services. If you prefer to keep searches local, you can disable the option to show cloud content.
To enable or disable cloud results in Search, use these steps:

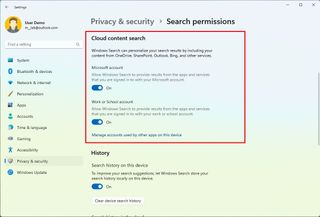
After you complete the steps, when performing a search, the system should show results based on your configuration.
Control search history settings
Windows 11 keeps a record of your queries to improve suggestions, but if you have concerns, you can always disable the feature or clear the search history.
To disable and clear the search history on Windows 11, use these steps:

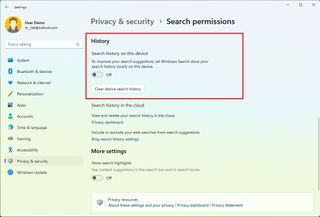
Once you complete the steps, Windows 11 will no longer store searches on your computer. (If you disable the feature, you must clear the history to delete previous searches.)
Control search highlights
Search highlights are the web content suggestions that appear next to the "Recent" list inside the Search interface. You can disable this feature if you don't want to see this content.
To disable content highlights in the Search interface, use these steps:

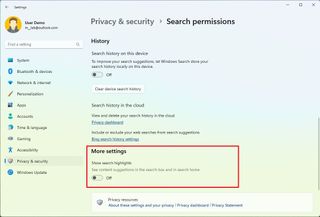
After you complete the steps, the next time you open the Search experience, instead of web content, you will find two lists, including "Quick searches" with suggestions to find settings and "Top apps" with the top six apps you use on Windows 11.
Windows 11 also include settings to manage the search behavior. For example, you can tell the system to slow down the indexing to preserve battery life. You can change the search mode, add and remove indexing locations, and more.
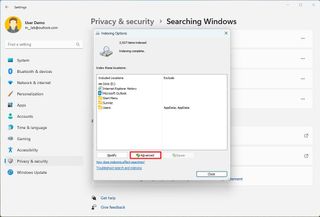
Check file indexing status
To check the current indexing status, use these steps:
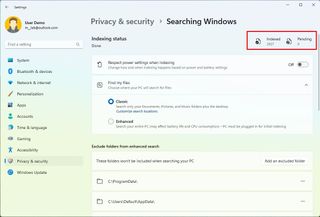
Once you complete the steps, the system will display the number of files that can appear on a search and any pending files for indexing.
Control search energy usage
The indexing process can take some time and consume extra energy, depending on the number of files on your computer. If you enable the power setting, the system will slow down the indexing to minimize battery usage, depending on your power settings.
To enable the power-saving option for indexing on Windows 11, use these steps:

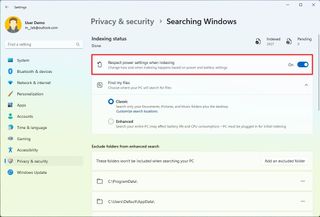
After you complete the steps, the Search feature will slow down the indexing process based on your power settings to preserve battery life.
Customize search locations
The classic search experience only scans and indexes specific known locations. However, you can add or remove other locations, including secondary and external drives and others.
To add or remove search locations on Windows 11, use these steps:

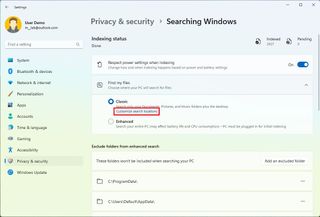
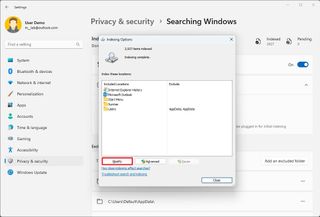
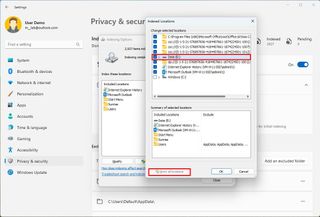
Once you complete the steps, the system will index the files in the specified locations to show search results.
Change search mode to enhance Search
Windows 11 offers two kinds of searches, Classic and Enhanced. The Classic mode only scans specific locations, and the Enhanced mode scans files in the entire computer. However, this mode will affect battery life and performance, and you must have the device plugged into a power source for the initial index.

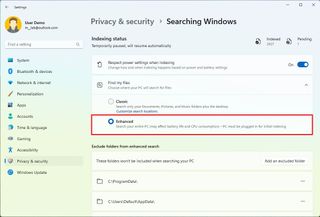
After you complete the steps, the system will index every file on the device, excluding those locations you specified with the instructions below.
Exclude folders
To exclude folders from the Enhanced indexing process on Windows 11, use these steps:

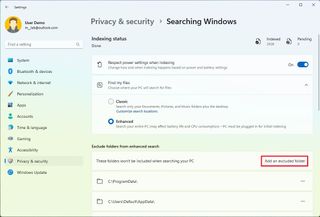
Once you complete the steps, Windows 11 exclude the folder locations and files from the search results.
This setting only applies to the "Enhanced" feature. If you use the Classic mode, you can exclude locations with the previous instructions outlined above.
Change advanced indexing settings
The Windows 11 indexing settings include some optional features that you can enable on your computer, such as the ability to index encrypted files and treat similar words with diacritics as different words.
To change the advanced indexing settings on Windows 11, use these steps:

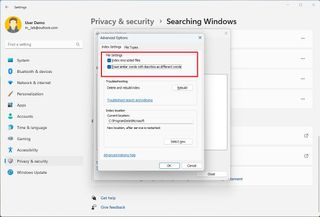
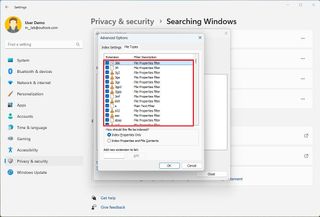
From the Indexing Settings tab, you can move the database to another location, but it's not an option you want to modify.
Search, like any other feature, can cause many problems on Windows 11. For example, it can cause high processor utilization and battery drainage. The database can get corrupted, causing unwanted behaviors, files may not appear in the results, and if something happens to the database, it can grow large, consuming large amounts of storage.
Whatever the issue might be, Windows 11 includes several ways to fix common problems.
Pause indexing
If the indexing process is taking a lot of system resources, you can always pause and resume at a later time.
To pause the indexing of files process on Windows 11, use these options.


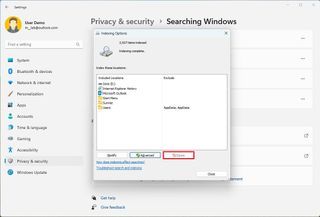
The option is only available if the system is processing and adding files to the database.
Troubleshooter
The Search and Indexing troubleshooter is a collection of scripts that allows you to automate the process of fixing problems seeing search results, the indexing process or search is very slow, and other problems.
To run the Search and Indexing troubleshooter on Windows 11, use these steps:

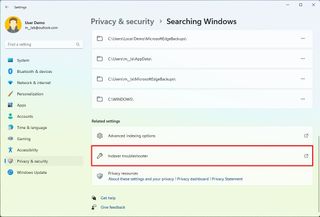
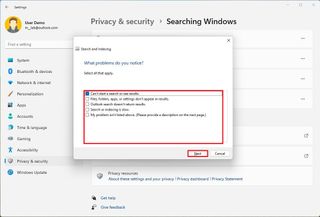
Once you complete the steps, the troubleshooter will run and resolve the problem.
Rebuild search index
If the troubleshooter doesn't resolve the issue, the index database has problems or taking a lot of space on the computer, rebuilding the index database may fix the problem.
To rebuild the search index to fix problems on Windows 11, use these steps:



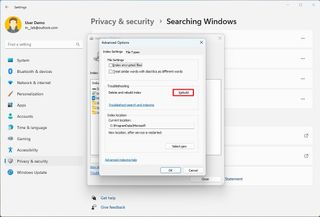
After you complete the steps, the system will delete the old database, and a new one will be created. Since the new database is empty, the indexing process will have to run again to catalog the files and make them available in searches.
For more helpful articles, coverage, and answers to common questions about Windows 10 and Windows 11, visit the following resources: